
menu

Posted in Uncategorized | February 2, 2023

Adenoids help protect the body from bacteria and viruses entering the mouth or nose. But they may sometimes become persistently enlarged and inflamed in the line of duty.
If this occurs, it can cause many issues, including breathing problems, sleep apnea, and chronic ear infections. Adenoidectomy, also called adenoid surgery, is a common procedure ENT specialists use to remove adenoids.
The procedure is a highly effective way to alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of constantly enlarged and infected adenoids. Keep reading to learn more about adenoids, when an adenoidectomy is necessary, and the benefits of removing adenoids.
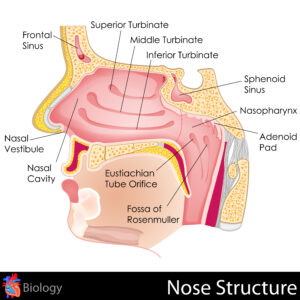
Adenoids are small glands that sit high at the back of the throat behind the roof of the mouth and the nose. It’s easy to confuse adenoids with tonsils.
But unlike tonsils, adenoids aren’t directly visible through the mouth or nose. Adenoids are one of the first lines of defense against infections in babies and younger children.
They make white blood cells that trap harmful viruses and bacteria when swallowed or inhaled. However, adenoids become less important as children age.
As their bodies learn to fight off infections, they may no longer need their adenoids. As they head into their teen years, adenoids begin to shrink.
Most people’s adenoids disappear entirely on their own by adulthood.
Although beneficial, adenoids can become enlarged or swollen when they fight off infections.
They may also become more prominent due to allergies. The swelling is sometimes temporary. But frequent infections, allergies, and other factors can lead to chronic enlargement.
Enlarged adenoids may cause unpleasant symptoms, which is why an ENT specialist at Specialty Care Institute may suggest your child should undergo adenoidectomy. Often, adenoids and tonsils are removed surgically at the same time.
When the adenoids become swollen, your child may have the following symptoms:

Adenoidectomy is the surgical removal of the adenoids. It’s important to note that your child’s immune system won’t weaken if they have their adenoids removed.
This is because adenoids are only a tiny part of your child’s immune system. Even if your child has their adenoids removed, their body has other ways to fight germs and bacteria.
Adenoid removal is performed by an ENT surgeon using general anesthesia. General anesthesia is quite safe. We will closely monitor your child throughout the procedure.
While the adenoids are at the back of the nose, the ENT surgeon can remove them through the mouth. A small tool is placed inside your child’s mouth to ensure it remains open.
The palate is then retracted, and the ENT surgeon uses a mirror to locate the adenoids. The surgeon scrapes away the adenoid tissue using Magill forceps and a curette, a tool shaped like a spoon.
The ENT surgeon can also choose to remove the adenoids using electrocautery. This technique uses heat to dissolve the gland and close the tissue left behind to stop the bleeding.
Another option for adenoid removal is the use of a microdebrider. In this method, the ENT surgeon creates an incision through the nose instead of in the mouth and uses the opening to remove the adenoid tissue.
The procedure takes about 20 to 30 minutes, and there won’t be visible scars after it’s over. After removing the adenoids, your child will remain in the recovery room until they wake up and are stable enough to be discharged.
You’ll receive medications to aid your child’s recovery. It’s normal for your child to have a mildly sore throat for a day or two after undergoing an adenoidectomy.
Most children can eat and drink normally within a few hours after adenoidectomy, even if their throat hurts a little. Ensure your child drinks lots of fluids to stay hydrated and reduce throat discomfort.
Typically, full recovery takes one to two weeks, but your child can resume their routine within a day or two. Sometimes, the adenoids can grow back after surgery and cause symptoms again. But it’s very rare for your child to require a second procedure.
Adenoidectomy can offer many benefits if your child is experiencing symptoms due to swollen adenoids. Some of these benefits include:

If your child’s adenoids become too big, they can partially block their breathing while sleeping. In severe cases, the adenoids may completely block the back of your child’s nose.
Adenoids that block the back of the nose cause loud snoring and sometimes lead to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). When your child has OSA, they stop breathing for a few seconds.
Pauses in breathing happen multiple times throughout the night, which may result in disturbed sleep. This can lead to growth, behavioral, learning, and heart problems. OSA might also cause persistent bedwetting in some cases.
Adenoidectomy significantly improves breathing, helps your child sleep better, and alleviates the symptoms of OSA.
Another reason why your ENT specialist at Speciality Care Institute may recommend adenoidectomy is because of persistent ear infections. The adenoids are found near the opening of the Eustachian tube.
Large adenoids can block the Eustachian tube, leading to middle ear infections, fluid build-up (also called glue ear), or even temporary hearing loss. An adenoidectomy removes the obstruction in your child’s Eustachian tube.
This helps restore normal Eustachian function and considerably reduces the number of ear infections.
If your child breathes through the mouth because of swollen adenoids, undergoing an adenoidectomy will help decrease mouth breathing.
Once the adenoids are removed, your child may still have throat infections, but they should have fewer.
Infected and enlarged adenoids harbor bacteria that cause bad breath. By removing the adenoids, you’ll eliminate the source of bacteria being produced, resulting in your child having better breath.

If your child has swollen adenoids, the experts at Specialty Care Institute can help. Our team will determine if an adenoidectomy is necessary to improve your child’s quality of life.
Do you think your child may need an adenoidectomy? Schedule your appointment at Speciality Care Institute in Arlington Heights, Barrington, Hoffman Estates, or Elgin, IL, now!